Time constant
Time constant
Learning objectives
- To know how to use a graphic method to determine the time constant of an electric circuit.
- To know the difference between transitory state and steady state.
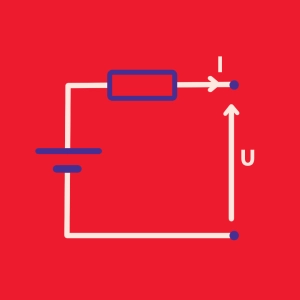
In an electrical circuit composed of a constant voltage source, E, in series with a resistance, R, and a condenser (capacitor), C, theory indicates that the response of the circuit to a voltage step, E, is a curve of exponential nature.
The exponential form is directly related to the values of R and C. Specifically the RC product that is homogeneous to a time (in seconds). τ = RC is called the time constant of the circuit. This is an indicator of the rate of change in the circuit experiencing a disturbance (by a voltage step). The smaller the value, the more rapidly steady state will be reached. The observation of the curve of voltage, or even the current, can approach the value of the time constant as illustrated in the animation.

Discover EduMedia for free
The interactive encyclopedia that brings science and math to life in the classroom.
Over 1,000 resources