 Speed controler for DC motor
Speed controler for DC motor
Learning objectives
- To explain the role of each component.
- To illustrate the influence of duty cycle on the output voltage, and so the speed of rotation of the motor.
- To teach the principle underlying the functioning of a switching power supply.
- To justify the appearance of each curve.
Transformers are powerful electrical components which enable the conversion of a sinusoidal voltage into another sinusoidal voltage of the same frequency, but with a different amplitude.
The physical principle of induction, which is the basis of the transformer, does not work with direct current (DC).
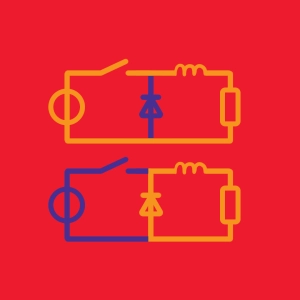
A chopper or Buck converter is analogous to a transformer, but it does work with direct current. A voltage, V, is reduced (stepped down) or increased (stepped up) to a different level of direct current.
We call this a DC-DC converter, as opposed to the transformer, which converts from alternating current (AC) to a different alternating current (AC-AC).
The chopper (Buck converter) underlies switching power supplies and the speed controllers for direct current machines.

Discover EduMedia for free
The interactive encyclopedia that brings science and math to life in the classroom.
Over 1,000 resources