Atoms, Ions and Molecules
Atoms, Ions and Molecules
Learning objectives
- To know the structure of an atom and a molecule.
- To define an electrical charge.
- To understand the phenomenon of the ionization of an atom.
- To know the difference between a valence electron and a free electron.
- To recognize two types of atomic bonds.
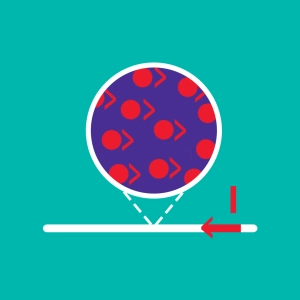
An atom is the smallest particle of matter that can combine chemically with another atom or molecule. It has a nucleus, composed of protons and neutrons, around which electrons orbit.
These particles have mass and another property called electric charge:
- The proton carries a positive one charge noted by +e
- The electron carries a charge equal to the proton but opposite in charge (-e).
- The neutron carries no charge and is therefore neutral
The number of protons in an atom signifies its name:
- 1 proton: Hydrogen
- 2 protons: Helium
- 17 protons: Chlorine
- …
An atom has as many protons as electrons. The total charge is zero which is why matter is usually neutral.
In some cases, with the help of an external energy input, an atom can lose or gain one or more electrons. This is the phenomenon of ionization.
Example: An atom of sodium (Na) has 11 protons and 11 electrons. If it loses an electron, it then has 11 protons but only 10 electrons. A positive charge +e is no longer balanced and the resulting sodium ion is positively charged. The sodium ion, Na+, indicates that it carries a charge +e.
A molecule is an assembly of atoms that share electrons to achieve greater stability.

Discover EduMedia for free
The interactive encyclopedia that brings science and math to life in the classroom.
Over 1,000 resources