 Synapse and ionic mechanisms
Synapse and ionic mechanisms
Learning objectives
- To understand nerve signal transmission at the level of an excitatory synapse.
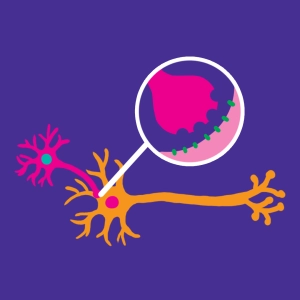
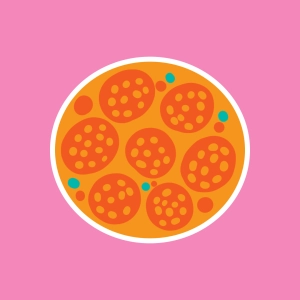
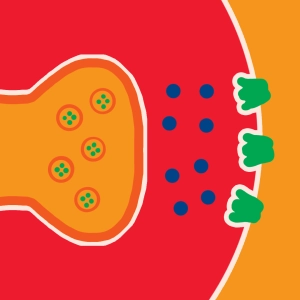
Synapse activity and related ionic mechanisms: Calcium ions flow into the presynaptique zone, through voltage-dependent channels, inducing exocytosis. Sodium ions flow into the postsynaptic neuron though receptors specific for a given neurotransmitter, inducing membrane depolarization.

Discover EduMedia for free
The interactive encyclopedia that brings science and math to life in the classroom.
Over 1,000 resources